Difference Between Ssd And Sshd
Sshd Vs Ssd Benchmark
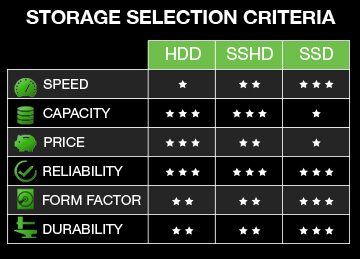
Hard disk drives were introduced by IBM in 1956, when they were used in a real-time transactions processing computer. As time passed they became smaller and smaller and the capacity went up drastically. As users are reporting, it takes some time for a SSHD to reach its maximum speed. And this is natural, as it learns what data is used the most. Solid State Drives (SSD)As memory got cheaper and cheaper it became economical to make storage devices from it. Today solid state disks are still expensive, but the future definitely belongs to them.They are made only from electronics (with no moving parts);.The reliability is still unknown as this is very young technology.They also have error correction code as the data written to cells is not perfect, as we may think.They are fast. They also have a different speed that depends on whether there a cache memory inside.Sometimes they are not compatible with older computer models.Samsung SSD.

What are the similarities?.All hard drives share the same interface, which is SATA.Earlier hard drives used to have a ATA interface.They drive almost the same amount of power. DifferencesSSDs not only store data differently from hard disk drives, but also employ new interfaces. For example, there are SSDs with PCIe and NVMe interfaces. Both interfaces allow for transferring data at much higher speeds. Some laptops have an option to use PCIe SSD in the place where the Wi-Fi card is connected.
ConclusionThe future definitely belongs to solid state drives (SSD), not just because they are faster, but they are simple as they do not contain any mechanical parts. As the electronics get cheaper we will see more and more SSD in our computers.Words like “amazing speed” is the right way to describe SSDs. They read the data at very high speeds. However, their data writing speed is a bit slower.My experience with SSDs has been positive. There was just one SSD that refused to run on an old Dell laptop, but that was probably because of the laptop’s incompatibility.What Do You Want To Read Next.
Hard disk drives were introduced by IBM in 1956, when they were used in a real-time transactions processing computer. As time passed they became smaller and smaller and the capacity went up drastically. As users are reporting, it takes some time for a SSHD to reach its maximum speed. And this is natural, as it learns what data is used the most. Solid State Drives (SSD)As memory got cheaper and cheaper it became economical to make storage devices from it.

Today solid state disks are still expensive, but the future definitely belongs to them.They are made only from electronics (with no moving parts);.The reliability is still unknown as this is very young technology.They also have error correction code as the data written to cells is not perfect, as we may think.They are fast. They also have a different speed that depends on whether there a cache memory inside.Sometimes they are not compatible with older computer models.Samsung SSD.
What are the similarities?.All hard drives share the same interface, which is SATA.Earlier hard drives used to have a ATA interface.They drive almost the same amount of power. DifferencesSSDs not only store data differently from hard disk drives, but also employ new interfaces. For example, there are SSDs with PCIe and NVMe interfaces.
Both interfaces allow for transferring data at much higher speeds. Some laptops have an option to use PCIe SSD in the place where the Wi-Fi card is connected. ConclusionThe future definitely belongs to solid state drives (SSD), not just because they are faster, but they are simple as they do not contain any mechanical parts.
As the electronics get cheaper we will see more and more SSD in our computers.Words like “amazing speed” is the right way to describe SSDs. They read the data at very high speeds. However, their data writing speed is a bit slower.My experience with SSDs has been positive.
There was just one SSD that refused to run on an old Dell laptop, but that was probably because of the laptop’s incompatibility.What Do You Want To Read Next.